Are you dealing with watery diarrhea and feeling overwhelmed and confused? You're not alone—watery diarrhea is among the most common gastrointestinal issues and a source of confusion for many.
This blog post will explain exactly watery diarrhea, its causes, symptoms to watch out for, treatments, and when to see your doctor. With this comprehensive overview, you'll have all the essential info you need to understand watery diarrhea better and take steps toward managing it if needed. Let's dive in!
Understanding Watery Diarrhea
Watery diarrhea is a gastrointestinal issue characterized by frequent, water-like bowel movements. Other symptoms can accompany it, including abdominal cramps and pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating, or fever. In some cases, its causes are easy to identify and treat. In others, it may require medical attention.
Most Common Causes of Watery Diarrhea
1. Infections
Bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections are the most common causes of watery diarrhea. Diarrhea caused by bacterial infections is usually accompanied by fever, abdominal cramps, and pain, whereas viral and parasitic infections may not cause additional symptoms.
2. Food Intolerance
Eating certain foods, your body cannot digest properly can lead to watery diarrhea. Common culprits for food intolerance include lactose, fructose, artificial sweeteners, caffeine, or alcohol.
3. Medications
Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can cause watery diarrhea as a side effect due to disrupting the normal gut flora or interfering with the digestion of certain foods.
4. Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder that affects the large intestine and can cause watery diarrhea. Other symptoms of IBS include abdominal cramps, gas, bloating,g and mucus in the stool.
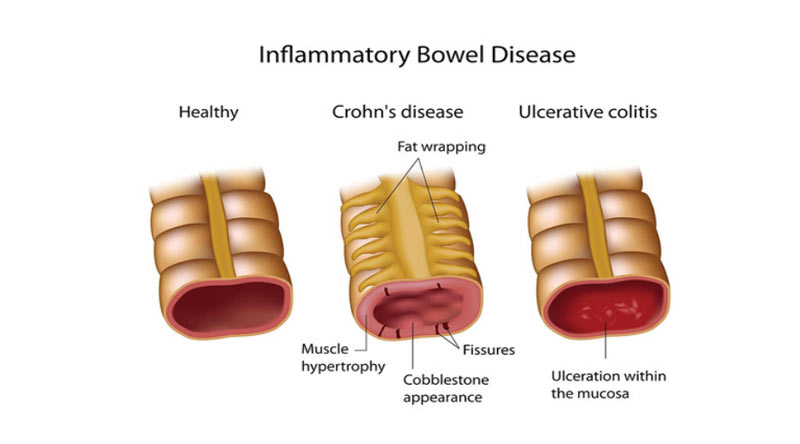
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease can cause watery diarrhea due to inflammation in the digestive tract. These conditions can be serious and require medical attention.
6. Stress or Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can cause changes in your body’s normal functioning, including digestion disruption, leading to watery diarrhea.
7. Malabsorption Syndromes
Malabsorption syndromes such as celiac disease or cystic fibrosis can cause watery diarrhea due to the body’s inability to absorb certain nutrients.
Watery Diarrhea Symptoms
1 Abdominal cramps or pain
This is usually the first symptom of watery diarrhea and can range from mild to severe.
2 Nausea
Nausea may accompany abdominal pain or occur on its own and can cause a feeling of sickness or even vomiting.
3 Bloating
Bloating can be caused by gas trapped in the intestines due to watery stools.
4 Fever
A fever may indicate an underlying infection causing watery diarrhea.
5 Fatigue
Watery diarrhea can be exhausting, leading to feelings of tiredness and exhaustion.
6 Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite is common with any gastrointestinal issue, including watery diarrhea.
7 Weight loss
Unintentional weight loss is a common symptom of watery diarrhea and can indicate that the condition requires medical attention.
8 Blood in stools
Bloody stools indicate a more serious problem and require prompt medical assessment.
Treatment for Watery Diarrhea
Treating watery diarrhea depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, it may resolve independently in a few days without any medical intervention, while in others, more aggressive treatment may be needed.
Dietary Changes and Medications
If food intolerance or malabsorption is to blame for your watery diarrhea, dietary changes can help alleviate the symptoms. Avoiding trigger foods and increasing intake of probiotics and fiber-rich foods can help restore the normal functioning of the digestive system.
Additionally, over-the-counter medications such as loperamide can reduce secretions from the gastrointestinal tract and provide quick relief from watery stools.
Antibiotics
If an infection is causing your watery diarrhea, antibiotics may be necessary to treat the underlying cause. It is important to take the entire course of antibiotics your doctor prescribes, even if your symptoms improve.
Causes Watery Diarrhea
- Infections
- Food Intolerance
- Medications
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- Stress or Anxiety
- Malabsorption Syndromes
- Parasites
Infections
Bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections are the most common causes of watery diarrhea. Symptoms may include fever, abdominal cramps and pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating, or fatigue.
Food Intolerance
Eating certain foods, your body cannot digest properly can lead to watery diarrhea. Common culprits for food intolerance include lactose, fructose, artificial sweeteners, caffeine, or alcohol.
Medications
Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can cause watery diarrhea as a side effect due to disrupting the normal gut flora or interfering with the digestion of certain foods.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disorder that affects the large intestine and can cause watery diarrhea. Other symptoms of IBS include abdominal cramps, gas, bloating, and mucus in the stool.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease can cause watery diarrhea due to inflammation in the digestive tract. These conditions can be serious and require medical attention.
Stress or Anxiety
Stress and anxiety can cause changes in your body’s normal functioning, including digestion disruption, leading to watery diarrhea.
Malabsorption Syndromes
Malabsorption syndromes such as celiac disease or cystic fibrosis can cause watery diarrhea due to the body’s inability to absorb certain nutrients.
Parasites
Protozoa, worms, and other parasites can cause watery diarrhea due to their presence in the digestive tract. Symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, vomiting, or bloody stools.
When to See Your Doctor for Watery Diarrhea
If you experience any of the following, it's important to see your doctor as soon as possible:
- Diarrhea lasting longer than two weeks
- Severe abdominal pain or cramps
- Significant weight loss without explanation
- Fever higher than 101 degrees Fahrenheit
- Blood in your stool
Additionally, if your symptoms do not improve after making dietary changes or taking over-the-counter medications, you should seek medical attention.
Steps to Avoid Watery Diarrhea
1. Practice good hygiene
Good hygiene is essential for preventing infections that can lead to watery diarrhea. Wash your hands regularly with soap and warm water, especially before eating and after using the restroom.
2. Exercise caution when traveling
If traveling abroad, be aware of the potential risk of food-borne illnesses and drink only bottled or boiled water to avoid contamination.
3. Monitor medications
Be aware of possible side effects of medications, including watery diarrhea, and consult your doctor if needed.
4. Choose healthy foods
Adopting a balanced diet with probiotics such as yogurt or kimchi can help maintain healthy gut bacteria levels and reduce the risk of watery diarrhea.
FAQs
Q: Are there any natural remedies for watery diarrhea?
A: Natural remedies can help manage symptoms of watery diarrhea. Probiotics, fiber supplements, and drinking plenty of fluids are all recommended treatments that may help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Some herbs, such as ginger, peppermint, and chamomile, have been known to relieve abdominal pain and cramping associated with watery diarrhea.
Q: What foods should I eat if I have watery diarrhea?
A: Eating foods that are easy to digest and low in fat can help reduce symptoms of watery diarrhea. Examples include plain white rice, cooked apples, bananas, toast, and oatmeal. drinkingFDrinking plenty of fluids is also important. Additionally, avoiding greasy or spicy foods may benefit some people with watery diarrhea. As always, it's best to consult your doctor before making any major changes to your diet, as they can provide personalized advice specific to your needs.
Q: Is there anything else I should know about watery diarrhea?
A: Yes! Many cases of watery diarrhea will clear up independently with simple dietary and lifestyle changes. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, you must see your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, practicing basic hygiene and handwashing habits is always a good idea to reduce the risk of developing watery diarrhea.
Conclusion
Watery diarrhea can be a confusing and overwhelming condition to manage, but with this comprehensive overview, you now have all the essential information needed to understand better what it is, its causes, symptoms to watch out for, treatments available, and when it's time to seek medical help. Remember to practice good hygiene, exercise caution when traveling abroad, monitor medication side effects, and choose a balanced diet to minimize your risk of developing watery diarrhea.