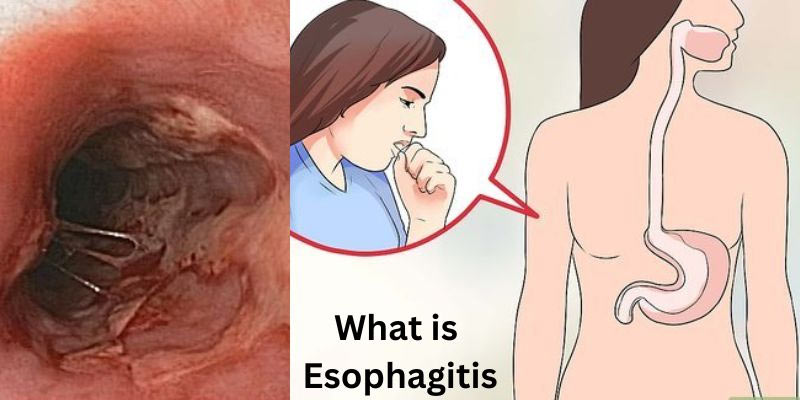
Are you having trouble swallowing or frequent heartburn? If so, it could be a sign of a disorder known as esophagitis. Esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus which can cause painful and uncomfortable symptoms such as burning in your chest, acid reflux, nausea, vomiting, and difficulty swallowing food. There are two main types of esophagitis – erosive and non-erosive – each with unique causes and treatments.
In this blog post, we'll explore what exactly esophagitis is, its associated symptoms, causes, and treatment options to help you better manage this condition if required.
Introducing Esophagitis
Esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus, the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach. Various things, such as irritation from certain chemicals or medications, infection, or injury, can cause it. Common symptoms include difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and heartburn. Other more serious symptoms may include bleeding in the esophagus, narrowing of the esophagus, or even a perforation in the wall of the esophagus.
Treatment for esophagitis varies depending on what caused it. It can range from making lifestyle changes to taking medications or undergoing surgery. Preventing esophagitis is also important and includes eating a healthy diet, avoiding smoking and other forms of tobacco use, and being aware of how certain medications may affect the esophagus.
If left untreated, Esophagitis can be a serious health condition, so it is important to speak with your doctor if you experience any associated symptoms. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan for you.
By understanding esophagitis's symptoms and potential causes, you can become better equipped to prevent and manage this condition. With the right care, you can reduce your risk of serious complications and live a healthy life.
Types of Esophagitis
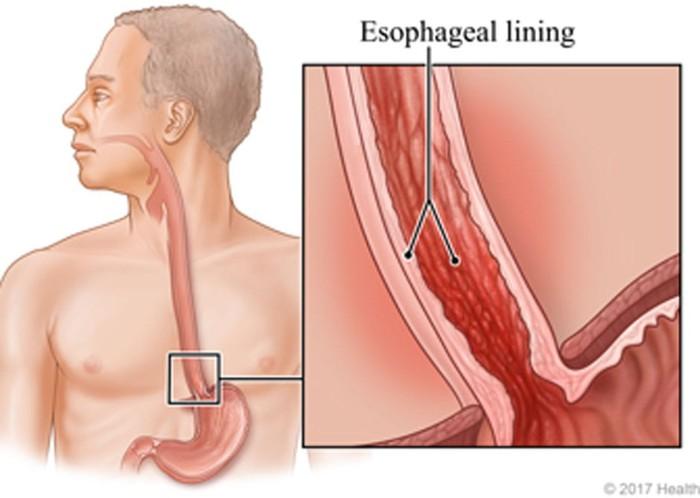
There are several types of esophagitis. The most common form is reflux esophagitis, caused by the backflow (reflux) of stomach contents into the esophagus. Other causes of esophagitis include allergies, asthmatic bronchitis, certain medications, and infections such as candidiasis (yeast), herpes simplex, or cytomegalovirus (CMV). In some cases, esophagitis is caused by a direct injury to the esophagus, such as radiation therapy.
Symptoms of esophagitis depend on the type and may include difficulty swallowing, chest pain or pressure, heartburn, nausea, and vomiting. Treatment for esophagitis generally involves medications, such as proton pump inhibitors or antacids, lifestyle changes (for example, avoiding certain foods that can worsen symptoms), and dietary modifications. In some cases, surgery may be necessary. It is important to seek medical advice if you experience any of the symptoms associated with esophagitis.
Lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and medications are all part of the treatment plan for esophagitis. It is important to consult your doctor to determine the best course of action for managing your condition. With proper care and management, you can reduce the symptoms associated with esophagitis and improve your quality of life.
Symptoms of Esophagitis
Esophagitis is an inflammation of the lining of the esophagus, which can cause various uncomfortable symptoms. These may include heartburn, pain or difficulty when swallowing (dysphagia), chest pain, nausea, and vomiting. Additional signs and symptoms of esophagitis may include sore throat, regurgitation of food or liquids, bad breath, hoarseness, and chest pain that worsens when lying down.
Esophagitis may be caused by various factors, including GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), viral infections, ingestion of acidic substances (such as lye), inflammatory conditions such as Crohn's disease, or overuse of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin and ibuprofen.
Treatments for esophagitis depend on the cause but may include medications, lifestyle changes, or surgery. It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any symptoms of esophagitis so that the underlying cause can be properly diagnosed and treated.
Diagnosis of Esophagitis
Esophagitis can be difficult to diagnose. Often, it is diagnosed based on the patient's symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing or chest pain. However, other tests can help confirm a diagnosis of esophagitis. These include endoscopy and biopsy, which allows for direct visualization and sampling of the esophageal tissue. Other tests, such as blood tests and imaging studies, can also be used to diagnose esophagitis.
Treatment for esophagitis usually involves lifestyle changes, such as avoiding food or drinks that trigger symptoms and quitting smoking. In addition, medications are often prescribed to reduce inflammation in the esophagus. If a bacterial infection causes esophagitis, antibiotics may be needed.
In severe cases, surgery might be required. It is important to seek medical care for any signs or symptoms of esophagitis to avoid further complications.
Treatments and Medications for Esophagitis
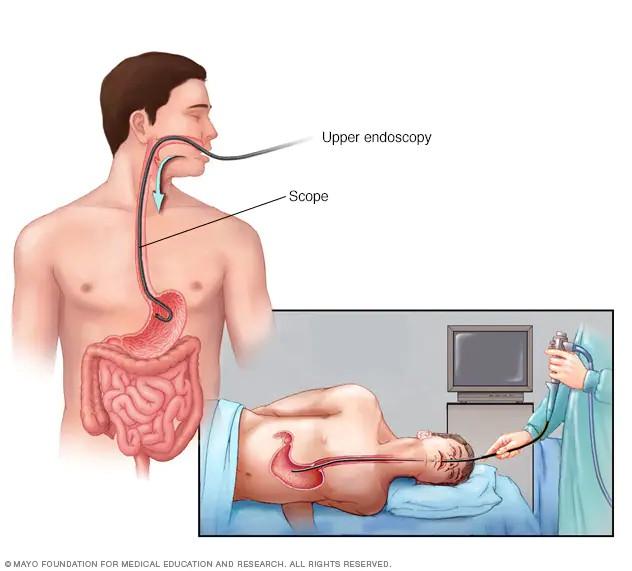
Esophagitis is typically treated with medications and lifestyle changes. Antacids, H2 blockers, proton pump inhibitors, and antibiotics are used to treat esophagitis. Lifestyle changes that can help reduce symptoms of esophagitis include avoiding foods or beverages that trigger an acidic reaction in the esophagus, eating smaller meals, and avoiding lying down after eating.
Surgery may also be an option for severe cases of esophagitis. The goal of treatment is to reduce the inflammation in the esophagus and improve the overall quality of life. Talking to a doctor about what treatment options are best for your situation is important.
In some cases, changes in diet and lifestyle may be enough to treat esophagitis. Eating smaller meals more frequently, avoiding acidic or spicy foods that may trigger irritation, and not lying down after eating can help reduce the symptoms of esophagitis. Additionally, quitting smoking and reducing stress can help manage the condition.
FAQs
What is the main cause of esophagitis?
Esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus, the muscular tube that carries food and liquids from your throat to your stomach. Various conditions, including acid reflux, infections, allergies, or some medications, can cause it. It is important to identify the underlying cause to effectively treat this condition.
How do you heal esophagitis?
Treatment for esophagitis depends on the underlying cause. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, medications to reduce acid production and inflammation, or antibiotics if an infection occurs. Surgery is sometimes necessary when other treatments cannot correct structural problems with the esophagus.
Can esophagitis be cured?
Esophagitis can usually be cured with the right treatment. Identifying and addressing the underlying cause is important to alleviate symptoms and help prevent a recurrence. Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery, depending on the nature of the condition. Your doctor can guide what treatments are best for your individual needs.
Conclusion
Esophagitis can be a very uncomfortable and bothersome condition; however, fortunately, treatments and medications are available to help relieve the symptoms. The most effective way to prevent esophagitis is by being mindful of aggravating factors that may increase your risk. As with any medical condition, you should talk to your doctor if you have any questions about esophagitis or its symptoms. Your physician can provide more specific advice on how to treat and manage esophagitis in your particular case.